Sep 09, · The Physics Behind Stopping a Car. We can use the kinetic energy idea, and a knowledge of driver reaction times, to write an equation that predicts car stopping distances ("stopping" distance is the sum of reaction and braking distance). Here is the equation's canonical form The ASTAR program calculates stopping power and range tables for helium ions in various materials. Select a material and enter the desired energies or use the default energies. Energies are specified in MeV, and must be in the range from MeV to MeV Oct 07, · Updated by: S.M. Seltzer and P.M. Bergstrom - both of PML Radiation Physics Division. Abstract: The databases ESTAR, PSTAR, and ASTAR calculate stopping-power and range tables for electrons, protons, or helium ions, according to methods described in ICRU Reports 37 and 49
Omni Calculator logo
Even if you're not a driver, you surely know that the car doesn't stop immediately after hitting the brakes. From the moment you spot a potentially dangerous situation, to the moment when the car comes to a complete stop, it travels a certain distance.
You can use this stopping distance calculator to find out how far your car travels in that time, depending on your speed, the slope of the road, and weather conditions. In this text, we will clarify the difference between the stopping distance and the braking distance, the physics of stopping. We will also explain how to calculate the stopping distance according to AASHTO the American Association of State Highway and Transportation Officials.
Imagine that you are driving your car on a regular street. Suddenly, you notice a child that runs across the street ahead of you.
What happens during the next few stressful seconds? First of all, the physics of stopping, some time will pass after the event began to happen, but before you react to it. This period is called the perception time.
During this time, the car continues to move with the same speed as before, approaching the child on the road. You might think that you hit the brake immediately, but there is always a small delay between the moment you notice the danger ahead and the instant in which you actually start to decelerate. This delay is the physics of stopping the reaction time, the physics of stopping. The car is still moving with the the physics of stopping speed.
After you start braking, the car will move slower and slower towards the child until it comes to a stop. The distance traveled from the moment you first hit the brake is called the braking distance. The stopping distanceon the other hand, the physics of stopping, is the total distance traveled during the perception and reaction time summed with the braking the physics of stopping. In the book "A Policy on Geometric Design of Highways and Streets", AASHTO gives the formula for calculating the stopping distance.
This formula is commonly used in road design for establishing the minimum stopping sight distance required on a given road. With correct parameters, it's a perfect equation for an accurate calculation of the stopping distance of your car. G is the grade slope of the road, expressed as a decimal. It is positive for an uphill grade and negative for a road going downhill. f is the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road, the physics of stopping.
It is typically assumed to be equal to 0. Most of the parameters in the formula above are easy to determine. You can have a big problem, though, when you try to estimate the perception-reaction time.
In the road design guidelines, AASHTO recommends the value of 2. In reality, many drivers are able to hit the brake much faster. You can use the following values as a rule of thumb:. Determine your speed. Decide on your perception-reaction time. Let's say that you had a good night sleep before the road, but have been driving for some time now and are not as alert as you could be.
You can set your perception-reaction time to 1. Is the road wet or dry? Let's assume it just rained, the physics of stopping. Embed Share via. Stopping Distance Calculator By Bogna Szyk. Table of contents: Stopping and braking distance How to calculate the stopping distance?
Perception-reaction time Calculating the stopping distance: an example. Stopping and braking distance Imagine that you are driving your car on a regular street. How to calculate the stopping distance? It is positive for an uphill grade and negative for a road going downhill; f is the coefficient of friction between the tires and the road. Perception-reaction time Most of the parameters in the formula above are easy to determine.
You can use the following values as a rule of thumb: 1 second - a keen and alert driver; 1. It is highly probable that also elderly or intoxicated drivers will manage to react within 2. Calculating the stopping distance: an example To determine the stopping distance of your car, the physics of stopping the steps below. Find out what is the slope of the road.
Perception - reaction time. The road is Stopping distance. Advanced mode. Check out similar physics calculators. Acceleration Acceleration of a particle in an electric field Air density … more. People also viewed…. Belt length The belt length calculator will tell you the length of a belt spread out between two pulleys.
Belt Length Calculator. Grams to cups The grams to cups calculator converts between cups and grams. You can choose between 20 different popular kitchen ingredients or directly type in the product density.
Grams to Cups Calculator. Plant spacing Planning out your garden? Try the plant spacing calculator. Plant Spacing Calculator, the physics of stopping. Pulley Pulley calculator finds all parameters of a belt drive system: the RPM, speed, belt length, belt tension, and torque. Pulley Calculator. Biology 59 Chemistry 57 Construction 89 Conversion 57 Ecology 21 Everyday life Finance Food 52 Health Math Physics Sports 71 Statistics 94 Other Discover Omni
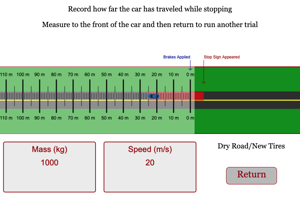
AP Physics Workbook 2.I Stopping Distance
, time: 7:36Description of PSTAR and ASTAR databases

At high energies, collision stopping powers are evaluated using Bethe's stopping-power formula (Bethe, ). At low energies, fitting-formulas are used which are based on experimental stopping power data. The boundary between the high- and low-energy regions was at approximately MeV for protons, and 2 MeV for alpha particles But although physics prevents us from creating a world where time doesn’t move, we can use physics to imagine what such a world would be like. Let’s assume for just a moment that you have The Physics Classroom» Physics Interactives» Work and Energy» Stopping Distance» Stopping Distance Interactive Using the Interactive The Stopping Distance Interactive is
No comments:
Post a Comment